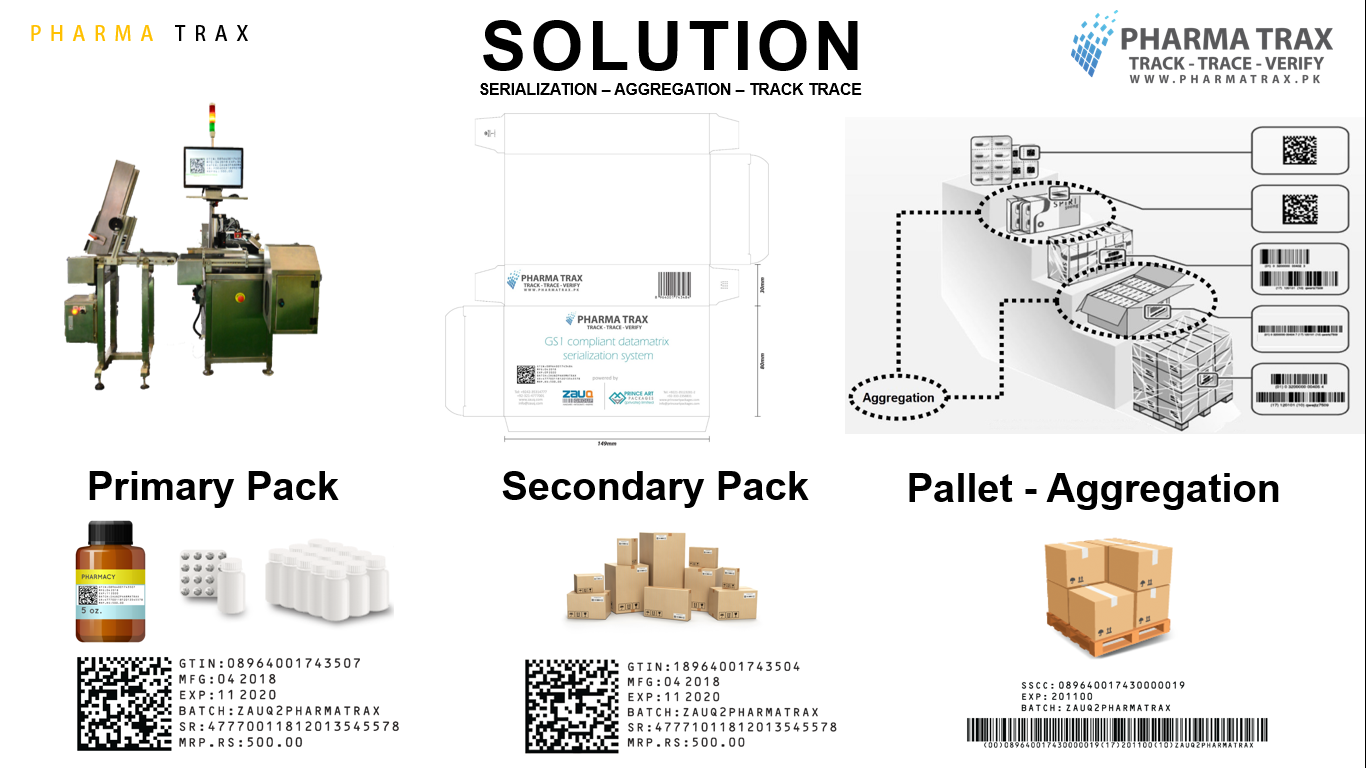
Product Details
Glyphosate, whose chemical name is N-(phosphomethyl)glycine, is an organic phosphine herbicide and a systemic conduction type broad-spectrum herbicide. Glyphosate is a non-selective, non-residual herbicide that is very effective against perennial root weeds. It is widely used in rubber, mulberry, tea, orchards and sugarcane fields. It mainly inhibits the enol acetonyl shikimidin phosphate synthase in plants, thereby inhibiting the conversion of shikilin to phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan, which interferes with protein synthesis and causes plant death. Glyphosate is absorbed by the stems and leaves and transmitted to various parts of the plant. It can prevent plants of more than 40 families such as monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous, annual and perennial, herbs and shrubs.